In today’s guide, we’ll be taking a comprehensive look at hydroponics, an accelerated soil-less growing method which – when done correctly – eliminates the mess of traditional gardening, while reliably germinating healthy plants.
What is hydroponics? What are the best hydroponic growing techniques for herbs, vegetables, fruits, or spices?
Follow along as we reveal all there is to know about this highly innovative and rapidly advancing method of gardening.
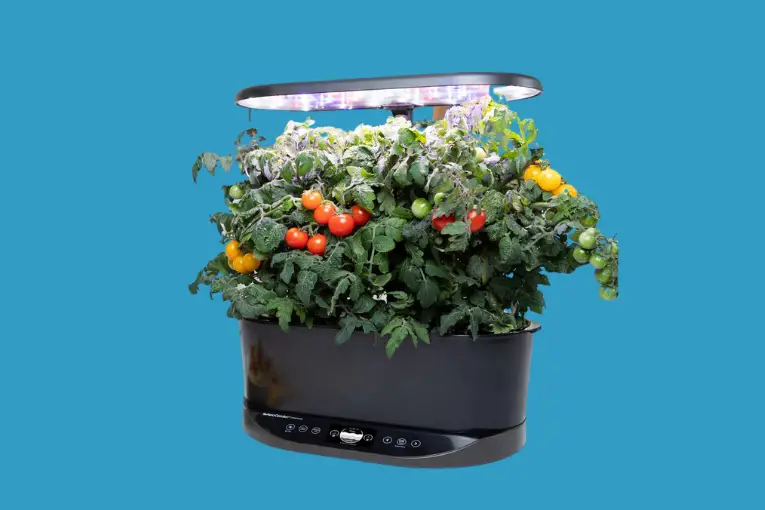
The Best Hydroponic System Overall: AeroGarden Bounty
It’s automated, inexpensive, aesthetically pleasing, and works remarkably well. The Bounty is my favorite hydroponic system overall.

Contents:
- What is hydroponics?
- Hydroponic Growing Techniques
- Best Hydroponic Herb Gardens Overall
- Liquid Culture Hydroponics
- Solid Media Culture
- Aeroponics
What is Hydroponics?
Although most of us often think about hydroponics in the context of state-of-the-art industrial grow rooms and innovative automated growing kits, hydroponics has actually been in practice for hundreds of years.
I’m referring to what was considered one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World – The Hanging Gardens of Babylon – which were (from what we can tell) hydroponically grown.
Very simply put, hydroponics is a growing method that requires no soil. Instead, plants are grown using a rich nutrient solution, sometimes with or sometimes without a growing medium (more on this later).

When using a hydroponic system, you’ll never need to worry about common soil-borne diseases or harmful pests.
Afterall, hydroponic techniques – when implemented correctly – offer a clean and controlled growing environment.
With that being said, within a controlled hydroponics growing environment, there are a few important metrics that must be consistently monitored:
- Proper Nutrient Solution: The nutrient solution that you use must be a concentration of all macro & micro-nutrients needed for optimal plant growth. Most commercial nutrient solutions fulfill these nutritional requirements.
- Proper Temperature and Aeration: Both liquid cultures and solid-media cultures require optimal temperature and aeration.
- Management of the Buffer Action: In hydroponics, the buffer action is simply the management of pH (acidity & alkalinity) and Ec (electrical conductivity) measurements for plant roots.
It’s worth pointing out that most commercial Aeroponic and model growing units automatically monitor and take care of these three metrics.
In this article, we’ll extensively cover both pre-made and commercial hydroponic units while also looking at some amazing DIY designs.
However, it’s important to know that building your own hydroponic set-up – especially an automated rig – is fairly difficult and requires a certain level of engineering knowledge.
Don’t get me wrong, there are many uncomplicated hydroponic techniques that you can build on your own with minimal experience – we’ll list a few later on – but for most people, an automated hydroponic kit is the best way to get started.
Hydroponic Growing Techniques
Hydroponics can be split up into three separate soil-less growing techniques:
- Liquid Culture Hydroponics: This technique uses a nutrient solution culture with no solid-medium. This includes various sub-techniques like the Nutrient Film Technique, the Ebb & Flow Technique, and the Deep Flow Technique.
- Solid-Media Culture Hydroponics: This technique uses a solid media and includes sub-techniques such as the Hanging Bag Technique and the Pot Technique.
- Aeroponics: Is a unique hydroponics technique where suspended plant roots are misted every few minutes for optimal aeration and moisture.
These sub-techniques can also be referred to as systems and are available pre-made, although most hydroponic heads prefer creating their systems from scratch.
The 5 Best Hydroponic Systems
- Best For Hobbyists: Deep Water Culture – Bubbler
- Best for Commercial Growing: Nutrient Film Technique
- Best Experimental Technique: Fogponics
- Best for Beginner: The AeroGarden Bounty
- Best for Budget: Deep Water Culture Starter Kit
The following table lists what we think are the best hydroponic systems. The table takes into consideration construction & upkeep costs, the difficulty of use or assembly, and growing performance for a cumulative score.
| System | Technique | Expenses | Difficulty | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Automated Indoor Herb Kits | AeroPonic | $$ | 1/10 | 98% |
| Nutrient Film Technique | Closed Liquid Culture | $$$ | 7/10 | 95% |
| Fogponics | Aeroponics | $$ | 4/10 | 93% |
| Hanging Bag Technique | Solid Media Culture | $$$ | 9/10 | 93% |
| Pot Technique | Solid Media Culture | $ | 5/10 | 91% |
| Root Dipping Technique | Open Liquid Culture | $ | 2/10 | 90% |
| Floating Technique | Open Liquid Culture | $ | 3/10 | 86% |
| Ebb & Flow Technique | Closed Liquid Culture | $$ | 5/10 | 84% |
NOTE:
Hydroponics originally referred to a single form of soil-less culture where plant roots are continuously suspended or misted by a nutrient solution. This would encompass both aeroponics and liquid hydroponics.
Solid-media culture, on the other hand, was for a long time just considered soilless culture as opposed to hydroponics.
For the purpose of this article and because most other sources refer to all three techniques as hydroponics, we will also refer to all three techniques as hydroponics.
Liquid Culture Hydroponic Growing:
Liquid Hydroponics – also called solution culture – can be broken down into two distinct systems, closed and open systems.
Systems that recycle excess nutrient solution – meaning nutrient solution that wasn’t absorbed by the plants – are called closed systems.
There are numerous closed system designs that one could implement; we’re going to cover the two most popular set-ups: the Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) and the Ebb & Flow Technique.
The following table shows the effectiveness, difficulty rating, and system type of two closed liquid hydroponic techniques: the Nutrient Film Technique and the Ebb & Flow technique.
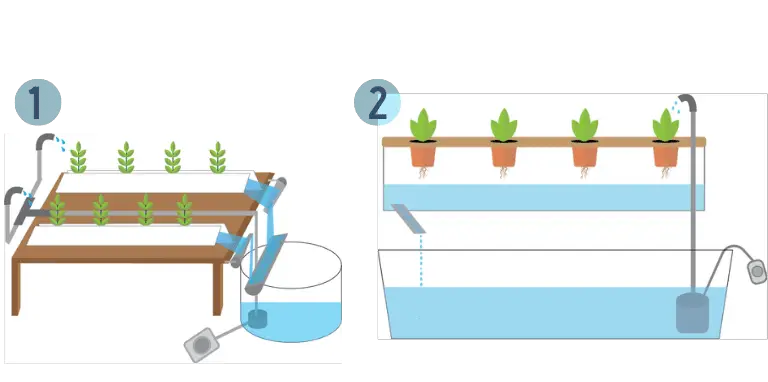
| Technique | Type | Difficulty | Effectivenes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Nutrient Film | Closed | 7/10 | 9/10 |
| 2. Ebb & Flow | Closed | 5/10 | 7/10 |
The Nutrient Film Technique
The Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) is perhaps the most reliable and popular hydroponic method.
The fundamentals are very easy to get your head around.
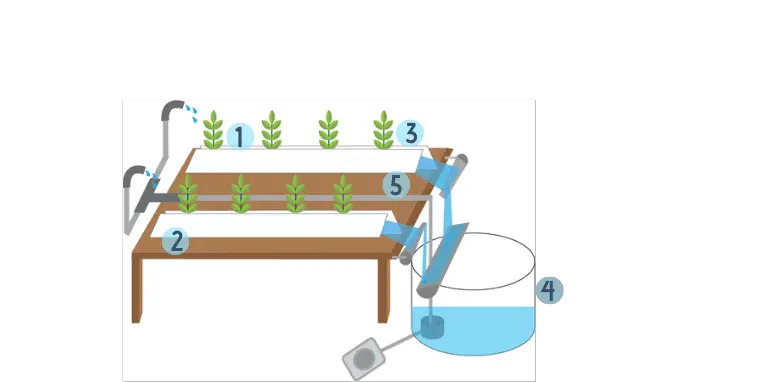
- The most important feature of NFT hydroponics is that plant roots are in direct contact with flowing nutrient solution.
- A flexible, yet sturdy thin sheet (up to 10 M in length) – with a sloping drop of up to 1 in 80 – acts as a channel for the nutrient solution. The solution runs from the top of the NFT unit to the solution container at the bottom (thank you gravity!).
- The seedlings with a growing medium – I recommend coconut coir – are placed between the flexible sheet with clips. As the nutrient solution flows from the top of the NFT unit, the growing medium should absorb the nutrients; as the plants grow, plant roots will firmly settle within the sheet.
- The solution tank collects the nutrient solution; most growers will monitor the solution’s pH balance and even replace it weekly.
- The nutrient solution is then recycled and pumped to the top of the NFT unit.
Now, as you probably suspect, this is a fairly advanced NFT design. There are much simpler set-ups –like this DIY unit from instructables – but the diagram above works well as a basic model for how the NFT functions.
The Ebb & Flow Technique
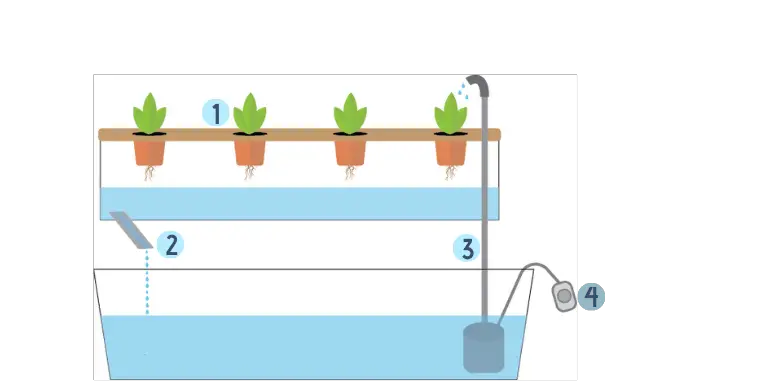
- Plants are placed in a fill-tray with a small amount of growing medium.
- Excess nutrient solution and water are dumped into the lower reservoir.
- A submersible pump recycles the nutrient solution and water from the bottom reservoir to the fill-tray.
- A timer is used to track flow rate.
The Ebb & Flow technique is a simplified version of the Nutrient Film Technique. It’s less expensive, easier to set-up, and roughly as efficient as the NFT.
Hydroponic techniques that do not reuse nutrient plant solution are called open systems.
The table below lists the two best open system hydroponic techniques by difficulty and effectiveness.
| Technique | Type | Difficulty | Effectivenes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Root Dipping | Open | 2/10 | 6/10 |
| 2. Floating | Open | 3/10 | 5/10 |
Open systems are arguably easier to set up than closed systems, but they don’t offer as much grow space and are usually less reliable.
I’ve personally avoided most open system designs as I feel automated hydroponic kits (especially aeroponic kits) are generally a much better alternative.
With that being said, let’s take a quick look at both techniques.
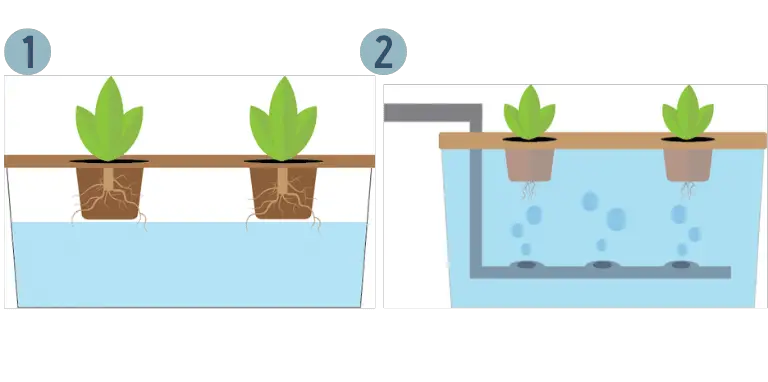
The Root Dipping Technique
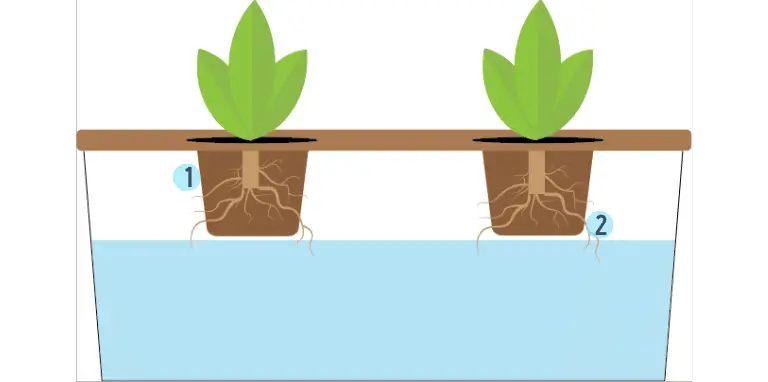
- Plants are grown in small netted pots with a little bit of growing medium. The pots should be submerged by roughly 2 – 4 cms.
- Some roots should be submerged, others should be suspended slightly above the reservoir.
This method takes less than an hour to set up. All you need are planting pots, seeds, some growing medium, a small container, nutrient solution, and a board used for holding the planting pots and covering the reservoir, along with a small hole at the top of the board for air passage.
The Floating Technique
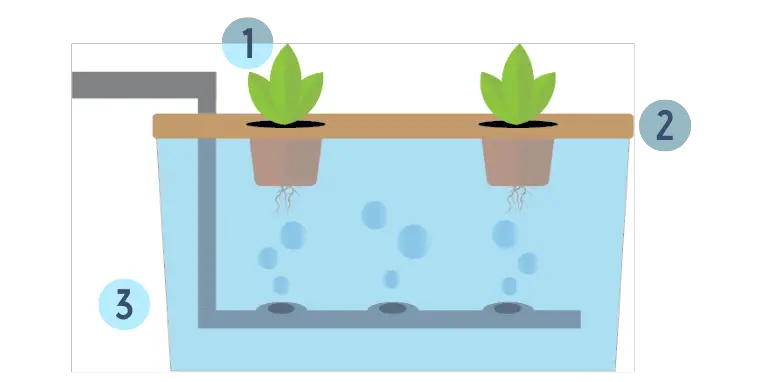
- Net pots are filled with a small amount of growing medium, along with seeds, and fitted to the top of a 30 – 40 cm styrofoam or wooden growing container.
- Plastic sheet or styrofoam lining to prevent water or liquid nutrient solution from leaking.
- Punctured PVC pipe filled with a growing medium for the early growing stages. As the plant roots grow, they will no longer need the growing medium.
Solid Media Culture
Solid media – like gravel, sawdust, coconut coir, rock wool, or vermiculite – are used in place of traditional soil in order to provide ample air and water to plant roots.
This method of hydroponics is often implemented by commercial growers as opposed to the everyday hobbyist. It’s for this reason that we won’t dive too deep into solid-media culture, but we will take a broad, quick look.
The following table lists our two favorite solid media culture methods:
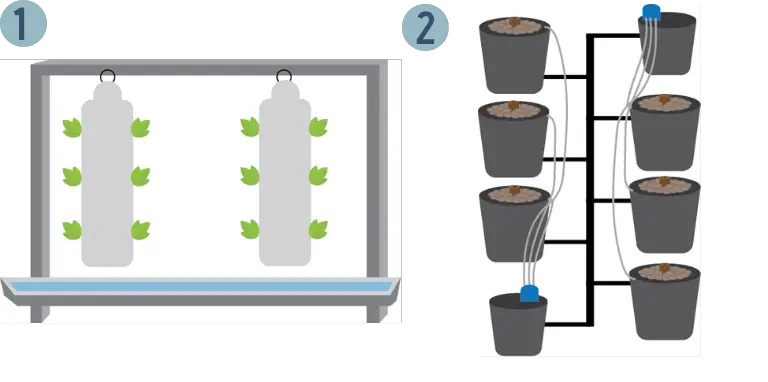
| Technique | Type | Difficulty | Effectivenes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Hanging Bag | Open | 9/10 | 10/10 |
| 2. Pot Technique | Open | 5/10 | 8/10 |
The Hanging Bag Technique is a fairly complex system that uses polythene bags – which are filled with a growing medium and tied to a PVC pipe from the top – to grow plants (usually herbaceous vegetation).
The pipe provides nutrient solution to the growing medium; excess solution funnels down to a lower reservoir where it is then recycled.
The Pot Technique – also known as the deep water culture technique – is classic. Clay or plastic pots are filled with a growing media; delivery pipes are then used to pump the nutrient solution into each pot.
Aeroponics

| Technique | Type | Difficulty | Effectivenes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Aeroponic Grow Unit | Aeroponics | 1/10 | 10/10 |
| 2. Fogponics | Aeroponics | 4/10 | 8/10 |
Admittedly, Aeroponics is my favorite hydroponic growing method.
In my personal experience, Aeroponic units are one of the most effective hydroponic techniques for growing herbs and vegetables.
Instead of plant roots soaking in a nutrient-rich solution like a few of the previously mentioned techniques, aeroponics is an active form of hydroponics where plant roots are suspended above a nutrient solution reservoir and are misted at optimal time intervals.
Aeroponics is ideal for low-growing herbs and vegetables (basil, spinach, tomatoes), but I have also grown small shrubs like honeysuckle successfully.
For a look at the best aeroponic kits, take a look at our chart above.
Best Hobbyist Hydroponic System – Deep Water Culture
Deep water culture systems are perfect for hydroponic enthusiasts that don’t want to bust the bank.
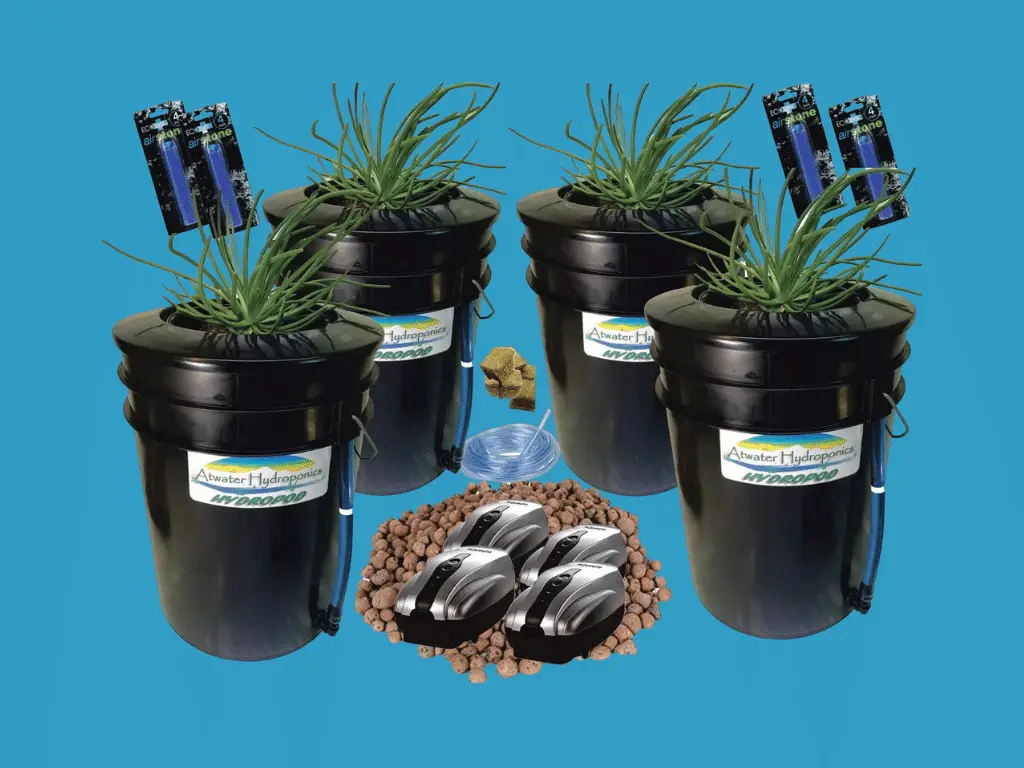

These systems use an air pump, grow stones, growing buckets, and a water indicator to create an ideal hydroponic growing environment for budding plants.
The small circular air stones used for most DWC systems are expanded clay pellets – an ideal, light-weight growing medium that gives plant roots plenty of air while still anchoring them in place.

Best Commercial Growing Hydroponics System – NFT Technique
We’re going to exclude the commercial hydroponic systems that cost hundreds of thousands of dollars and instead focus on the best small scale commercial hydroponic systems.
Our pick is the Nutrient Film Technique.

The WEPLANT system uses a timed circulation process for optimal nutrient dissemination.
Although this system differs from the larger scale, commercial NFT systems, it still works well for a mid-sized growing operation.
Best Experimental Hydroponics Technique – Fogponics
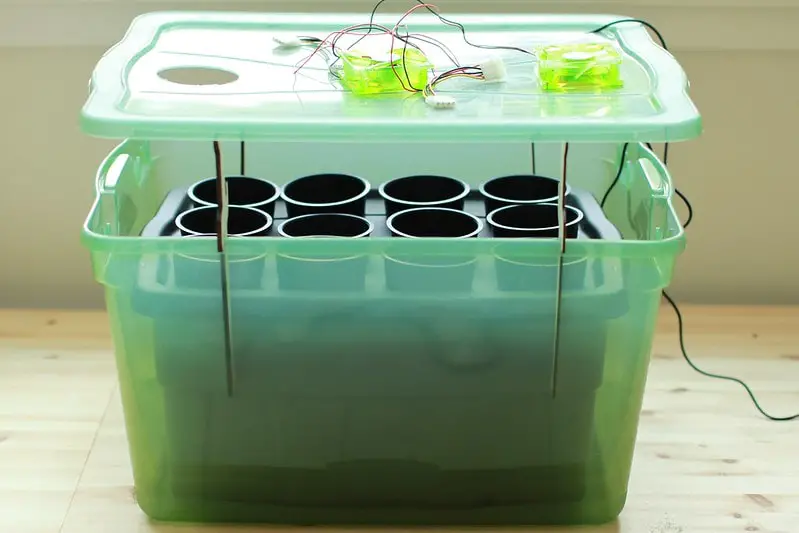
Fogponics is an aeroponic growing technique that implements an ultrasonic fogger to dispense nutrient solution to plant roots.
The main idea is that plant roots absorb super small nutrient solution particles better than larger nutrient solution particles.
Check out this comprehensive D.I.Y Fogponics design video:
Best Hydroponic System for Beginners – AeroGarden Bounty
If you’re looking for a quick hydroponic system that requires minimal upkeep and work, look no further than the 9-pod AeroGarden Bounty.
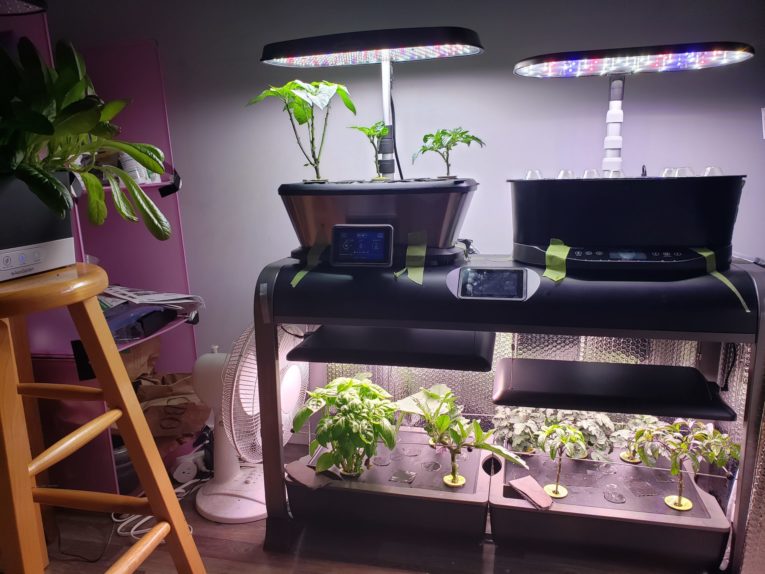

We covered Aerogarden extensively and found a lot to like.
The Bounty is really easy to use and loaded with everything you need to get growing right away.
- An automated grow feature w/ watering reminders.
- Plenty of growing space.
- A 24″ tall adjustable grow lamp with a mixture of red, white, and blue LED grow lights for all stages of plant growth.
- A wide variety of planting pods for various herbs and vegetables.
Best Budget Hydroponic System – Deep Water Culture Starter Kit
As you can tell, we’re big fans of DWC hydroponic systems and they just so happen to be excellent starter systems.
This DWC system by SavvyGrow is an excellent introduction to soil-less growing with everything you need to get growing right away:

- Air pump.
- Rockwool growing media.
- Net cups.
- Clay airstones.
- Medium-size DWC grow-reservoir.
If you’re not into the automated aeroponic systems, this DWC is worth a try, especially for those of you wanting to grow lettuce, tomatoes, and spinach.

